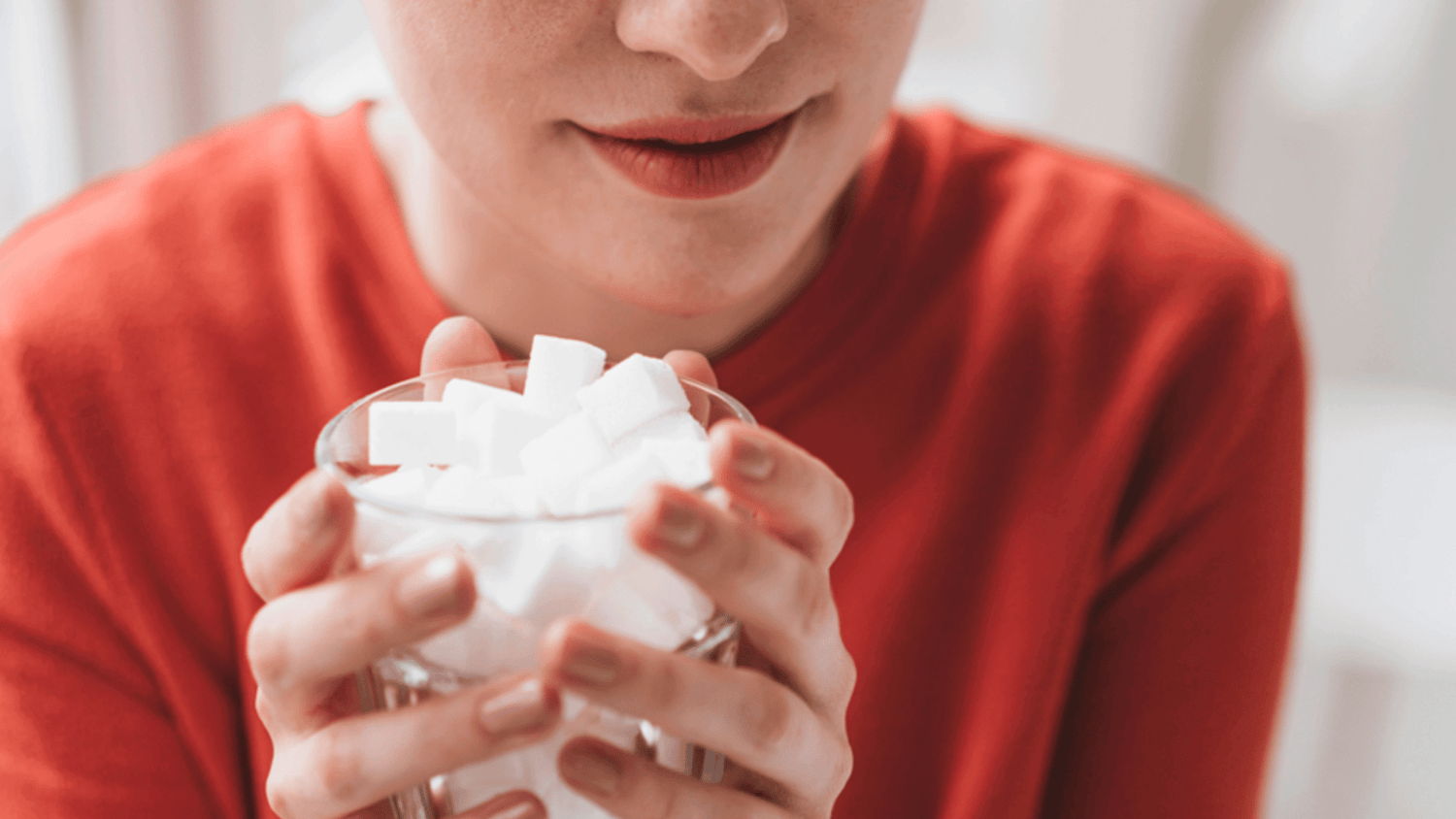
Sugar’s Effects on Skin: Glycation and AGEs
Aging is a natural process, but excessive sugar speeds it up in multiple ways.
When sugar enters the bloodstream, it binds to proteins like collagen and elastin through a process called glycation, forming harmful molecules known as Advanced Glycation End Products (AGEs).
These AGEs damage your collagen and reduce skin elasticity, increasing visible signs of aging. Additionally, AGEs increase oxidative stress and inflammation, which further weaken the skin’s structural integrity and resilience.
In addition to glycation, high sugar accelerates aging by damaging protective caps on DNA called telomeres, which shorten as cells divide. This shortening process is a natural part of growing older, but excessive sugar intake speeds up telomere shortening, further contributing to premature aging.
Key effects of sugar on the skin include:
- Loss of Firmness: Glycation breaks down collagen and elastin, causing sagging skin, especially around the chin and neck.
- Fine Lines and Wrinkles: AGEs stiffen collagen, making skin less flexible and therefore more prone to fine lines and wrinkles.
- Inflammation: Sugar-related glycation can worsen acne and redness by increasing inflammation. This can lead to clogged pores and increase risk of breakouts.
- Oxidative Stress: High sugar intake elevates oxidative stress, accelerating overall skin cell damage.
- Dehydration: Excessive sugar can dehydrate skin by drawing water out of cells, leading to dryness, dullness, and an increase in visible fine lines.




























1 comment
Susan
Cosmetic or plastic surgeon
———
KaramMD Skin replied:
Hi Susan—Dr. Karam is a facial plastic surgeon. You can learn more about his clinical practice on his website drkaram.com.
Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.